They discover an area on Mars that could have been repeatedly habitable until relatively recent dates
Clay deposits suggest a breeding ground for life on Mars.
Clay deposits observed in the Margaritifer region of Mars could have been repeatedly habitable until geologically relatively recent dates in Martian history.
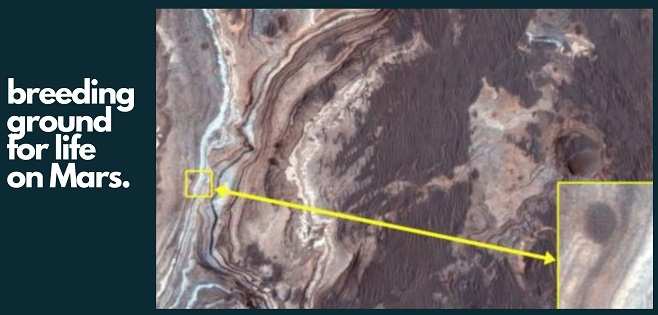
Clayey deposits connected to sediments were revealed by data from NASA’s High-Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE), Contextual Camera (CTX), and Compact Reconnaissance Imaging Spectrometer for Mars (CRISM) missions. Stratified riverine on the uplands around the Ladon Basin, southern Ladon Basin, and the northern Ladon Valley.
Catherine Weitz, a scientist at the Planetary Science Institute (PSI) and a HiRISE co-investigator, said in a statement that the presence of fluvial sediments in layers containing clays indicates that the environment was conducive to life, as clays form and remain stable under neutral pH conditions, where water persists for a long period.
A ravine on Mars
Previously the same spacecraft had surveyed a ravine on Mars. Ditches or gully landforms are common on Mars, especially in the southern highlands.
A couple of images showed that material flowing down a gully head came from an older path and eroded a new channel.
The dates of the images are more than a full Martian year apart, so the observations do not pinpoint the season on Mars that this site showed activity.
Related Post
